Epilepsy syndromes
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
-
One of the most common epilepsy, 8 - 18 岁
-
Usually in the early morning, soon after awakening.
-
Traid(单独或同时出现):
-
Myoclonic seizure(Bilateral symmetrical myoclonic jerks, without impaired consciousness)
-
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures -> happens in the context of sleep deprivation or alcohol ingestion
-
Absence seizures with impaired consciousness
Least common
-
Triggers: sleep deprivation, alcohol consumption, flickering lights
-
EEG: Irregular 3–5 Hz polyspikes and waves with frontocentral predominance
-
治疗: valproic acid
-
Responds well to antiseizure drug, Life-long treatment usually required (high risk of recurrence)
Juvenile absence epilepsy
- 9 - 13 青春期,男女相同
- 失神发作:少于 childhood absence epilepsy
- 80% 有 Tonic-clonic seizures -> valproic acid 为1线治疗
- 预后较好,60%治疗后无发作,可转化为Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
Childhood absence epilepsy
-
6-7岁,女孩多见,遗传
-
失神发作
-
lasting 5–10 seconds,发作频繁,up to 100x/d
-
无肌阵挛
-
Amnestic during seizures
-
Lip smacking, eye fluttering or head nodding are common
-
-
非典型失神发作:more gradual onset and ending, duration of > 30 seconds.
-
Triggers: hyperventilation, lights
-
治疗:Ethosuximide, 预后好,80%药物治疗后无发作
★九版书为 sodium valproate
Both ethosuximide and sodium valproate have a similar efficacy in preventing absence seizures in childhood absence epilepsy. However, the risk of attentional dysfunction is higher with sodium valproate than ethosuximide.
Symptomatic or cryptogenic generalized epilepsy syndromes
These syndromes do not respond well to antiseizure drug therapy and are commonly associated with developmental delays, as well as motor and cognitive impairments.
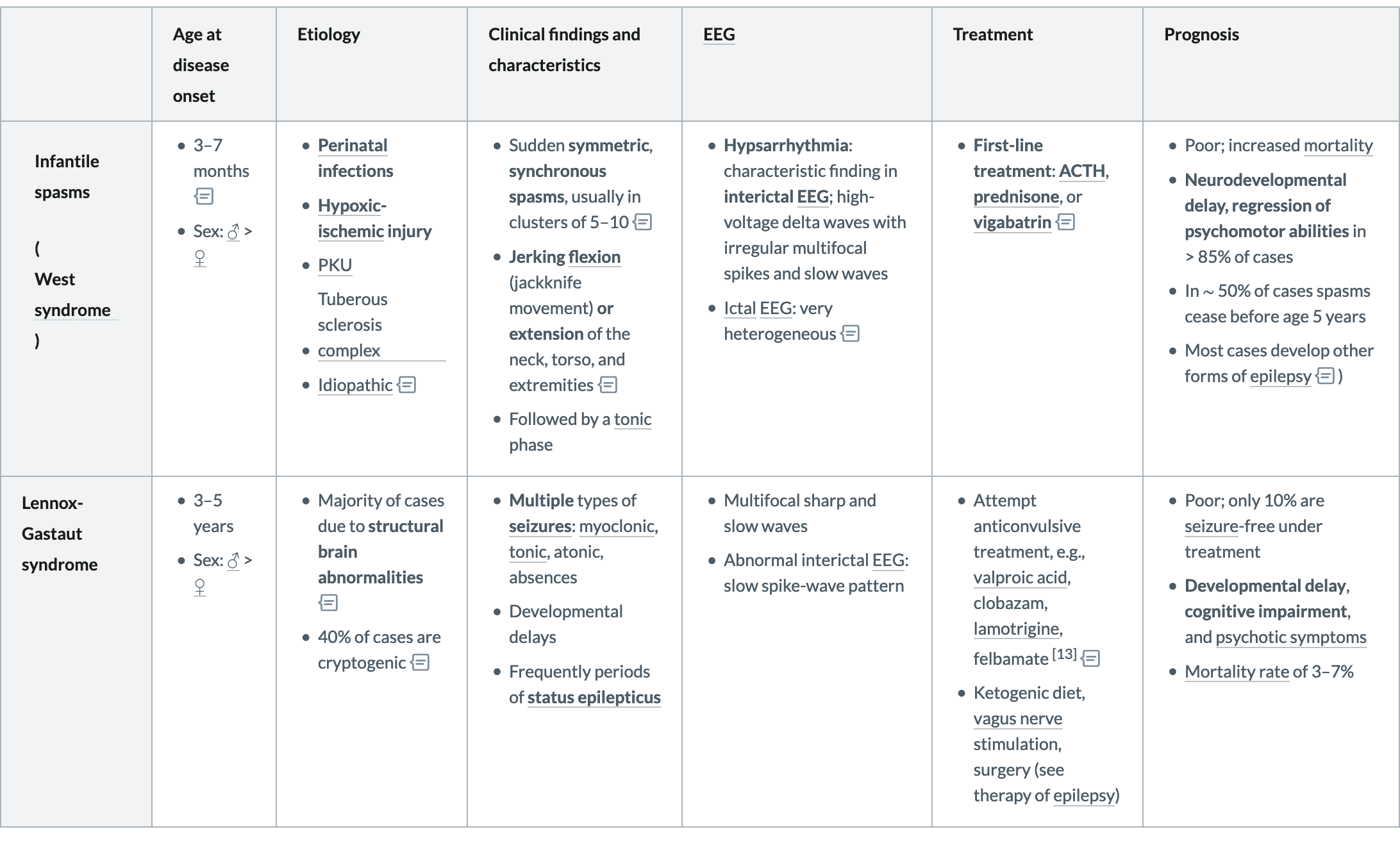
Infantile spasms(West syndrome)
- 3–7 months(1年内发病)